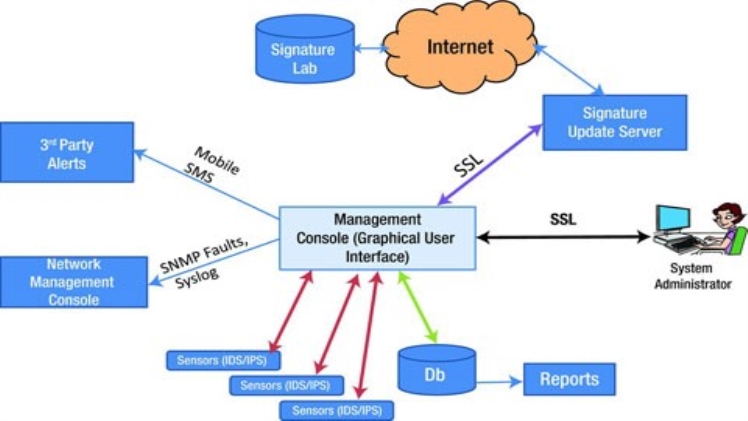
It is harder for organizations to identify malicious traffic because it is evolving and changing fast. The traffic accesses the system through links, files, or connections created or received through the network. The traffic pauses a threat to an organization that can create a big impact on its security and compromise data. IT experts identify malicious traffic through analysis of the communication it performs within the network. They use machine learning and train it to detect or identify malicious traffic/activities.
What is malicious traffic?
Malicious traffic is defined as a suspicious link, network connection, or file developed or received in a network. After being developed or received, the traffic causes an incident that compromises the data security of the organization. HTTP traffic is considered the commonest and most dangerous type of malicious traffic. It mostly comes through non-browser apps and then attaches itself to control servers or bad command URLs. When HTTP successfully connects to remote servers, it takes control and wreaks havoc on the system, including:
- Delivering more malware into the system
- Executing further commands in the server
- Communicating with botnets
- Commands for download or upload of files
- Infiltration of sensitive data
- Updating applications with their codes
A cybersecurity report by Check Point shows cyberattacks against organizations in 2021 increased by 50% compared to the 2020 figures. The most targeted sectors were research and education, which recorded an average of 1,605 attacks every week. Attacks against software vendors in 2021 increased by 146%.
In early 2022, many organizations experienced the Great Return as they called their employees to return to full-time work. Most of them adopted a hybrid work structure or remote model. Cybercriminals acted swiftly and began launching unprecedented attacks. Organizations need to work closely with web security services to improve their online security structures.
One of the security measures they implement is browser isolation, where a user’s browsing activity is separated from the server network. Perception Point offers an Advanced Browser security engine that isolates, detects, and remediates malicious threats from the web.
How malicious traffic works
Malicious traffic accesses an organization’s network through incoming requests, connections, or files that connect themselves to untrusted sources. If it succeeds without detection, it begins to execute its purposes. Its codes can access the target system in the form of the following:
- Malicious data files: Files that cannot be executed, such as PDF, MS Word, and Zip files.
- Viruses: They are executable and have the potential to damage files within the system.
- Trojans: Programs that hide harmful viruses or programs. They begin executing from the background and are hard to detect.
- Worms: Viruses that self-propagate from one system to the next.
After a successful attack, cybercriminals begin to take control of servers from their remotely located command and control servers. They send different types of commands which are executed into the target system. The latest cybersecurity trends show that in the evolution of IT infrastructures, there is an increase in the number of entry points for attacks. They can happen through user access, mobile devices, IoT, networks, and cloud devices. To improve security, organizations are taking different measures.
- Cloud-native app protection platforms: All cloud security capabilities are put into a single security solution.
- Security consolidation: Use of security solutions developed by one vendor for better efficiency and visibility.
- Hybrid data centers: Adaptation of both cloud-based and on-premise security infrastructure.
- Mesh architecture: Consolidation of multiple security components such as:
- Consolidated dashboards
- Consolidated posture/policy management
- Security analytics and intelligence
- Distributed identity fabric
How to detect malicious traffic
Several tools and strategies are used to detect malicious traffic that intrudes on computer networks. One of the widespread detection techniques is machine learning. It is configured to feed the Intrusion Detection System to effectively detect all malicious traffic networks. Machine learning is first trained using large sets of data generated from malicious and non-malicious traffic. Other types of tools used for detecting malicious traffic are:
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Protects sensitive data such as credit card information from detection by malware.
- Intrusion Prevention System (IPS): Keeps track of weak network points and generates analyzed reports, and also blocks malicious activities to protect the system.
- Security Incident and Event Management (SIEM): Manages all data and signals and generates data on potential threats into a single view.
- Network Behaviour Anomaly Detection (NBAD): Monitors and looks for activities that are not ordinary.
- Intrusion Detection System (IDS): Keeps track of weak network points and generates analyzed reports.
How to prevent malicious traffic
SonicWall reports that it identified more than 270,000 new malware variants in the first half of 2022. Compared to the same period in 2021, this was a 45% increase. On average, 1,500 new malware variants were released daily. This raises the alarm to organizations on the importance of preventing malicious traffic from accessing their systems. They can use various sets of strategies and tools.
Secure authentication
Use of multifactor authentication such as codes and security questions combined with passwords. Adopt the use of biometric tools such as voice detection, eye scans, facial detection, and fingerprints. Use a password manager to store passwords.
Anti-spyware and anti-virus software
Anti-spyware and anti-virus software scan computer systems and files to detect and remove malware. The tools need to be updated all the time and to run scans often. The tools cannot provide organizations with total protection.
Use controlled systems access
Organizations can use multiple ways to control access to their systems. Before software installation, understand the licensing agreements. Use detection tools such as IDS, IPS, and firewalls. Keep all unused ports closed and remove all unused user accounts. Avoid installing unfamiliar remote drivers.
Use email security and spam protection
Email is the main communication tool in most organizations, but it is prone to malware attacks. Protection tools scan incoming and outgoing emails for malware, spam, and links.
Security awareness
Implement continuous security training sessions for all workers to create awareness. Training helps reduce the chances of attacks due to employee errors. It helps keep employees updated with the latest trends, best security practices, and how to detect unusual behavior in the system.
Conclusion
Malicious traffic attacks computer networks and then steals, deletes, or encrypts data. It can introduce spam, force ads, alter systems functions, or extort money. HTTP is the commonest and highly dangerous form of malicious traffic. It can be prevented by implementing advanced security measures. Organizations should use secure authentication, control systems access, and create employee security awareness.